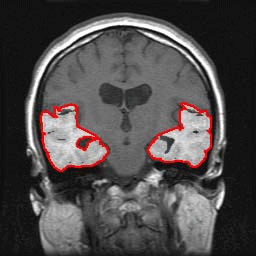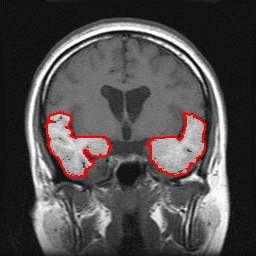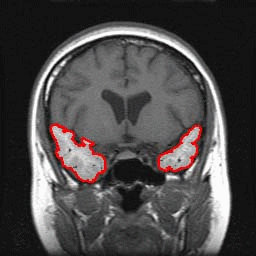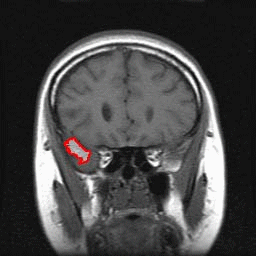
Automated Segmentation of the Temporal Lobe and Volumetry from Brain MR Images
Norio Hayashi
Background
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is replacing CT (computed tomography) as the defacto standard used to evaluate patients with suspected temporal lobe abnormalities since the MRI technique measures the changes in the volume of the brain, which is an important diagnostic indicator for temporal lobe-related abnormalities. Another reason is that the contrast quality of MR images better identifies organic anomalies and slight changes in volume. In the case where a patient suffers from premature dementia such as early stage Alzheimer’s disease, a volume reduction of the temporal lobe often occurs. Other diseases such as schizophrenia shrinks the parahippocampal gyrus and expands the lateral ventricle. However, it has been difficult to detect the slight abnormal changes of the temporal lobe. Thus, we have attempted to quantitatively estimate such slight changes in volume of temporal lobe.
Research
This study used C ++ computer language to develop a technique to automatically recognize the slight volume changes of the temporal lobe from MR images.
|
|
|
|
|
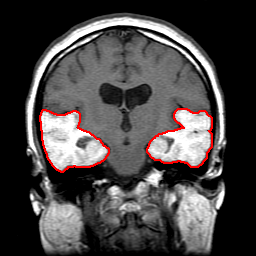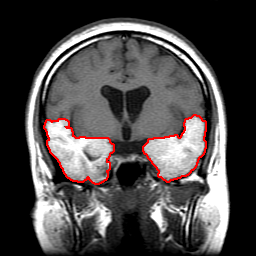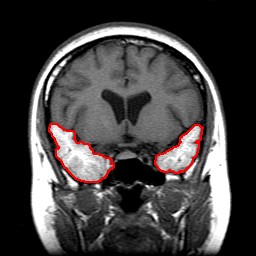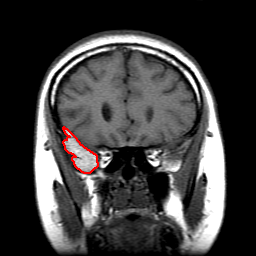
Automated Segmentation |
|
Manual Tracing |